Duties of Governmental Entities
Midterm Prep Wrap-Up
Responses to student questions:
- How do we connect to core values?
- What supplements should we use?
- How do we structure an exam answer?
How do we connect to core values?
What supplements should we use?
For Review:
- Understanding Torts
- Gilbert Law Summaries: Torts
For Practice Problems:
- Tort Law and Practice
How do we structure an exam answer?
Two parts:
- Personal notes: organized and exhaustive
- Actual answer: organized and selective
Practice Question Structure: Personal Notes
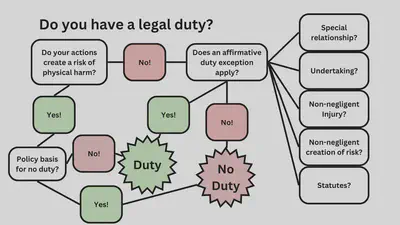
Structure: Actual Answer (Example)
Main Issue
- Introduction
- Rule
- Analysis
— Subissue # 1
— Rule
— Analysis
— Conclusion
— Subissue # 2
— Rule
— Analysis
—— Sub-subissue
—— Rule
—— Analysis
—— Conclusion
— Conclusion
- Conclusion
Practice Question Structure: Actual Answer
- Introduction (basically your holding / conclusion)
- Rule for duty
- Acknowledgment that this is a close call and both paths will be analyzed.
- First path: Actions created a risk of physical harm
— Rule
— Analysis
—— Subissue: Policy basis exception
—— Rule
—— Analysis
— Conclusion
- Second path: Affirmative duty
— Rule
— Analysis
—— Subissue: Exceptions
—— Rule
—— Analysis
———— Subissues: Each exception that warrants a full analysis
———— Rule (when does this exception apply?)
———— Analysis
— Conclusion
- Conclusion
Duties of Government Entities
Riss v. City of New York
Riss v. City of New York
Proprietary functions
vs.
Governmental functions
[fit] Because we owe a duty to everybody, we owe it to no one.
Rationale for no governmental duty
- Lack of expertise (judge & jury)
- Separation of powers
- Limited government resources
Lauer v. City of New York
Lauer v. City of New York
Discretionary functions
vs.
Ministerial functions